What is a SENSOR ? Definition, uses and types of sensors
I. What is a SENSOR ?
1. A sensor is an electronic device that can detect, sense and respond to changes in the surrounding environment.
They convert physical quantities such as temperature, light, pressure, sound, motion, etc. into electrical signals for processing and making control decisions.

2. What is the general structure of a sensor?
The structure of a sensor is usually a complete, miniaturized system, including electrical circuit elements that are closely connected together. The signals received from the environment after processing will be standardized to the most suitable voltage and current levels for transmission to the central controller.
3. The role of sensors
In each field, sensors play different important roles:
– Industry: Monitor and control the production process, ensure labor safety and improve operating efficiency.
– Healthcare: Diagnose diseases, monitor patient health and support treatment.
- Environment: Monitoring environmental pollution, forecasting natural disasters and protecting natural resources.
- Agriculture: Automating irrigation systems, fertilization and disease control.
- Home: Automating electronic devices, improving comfort and saving energy.
II. How does the sensor work?
The sensor works on the principle of magnetic field. When powered, the current flows through a circuit with an inductor, when a magnetic field passes through the circuit, the sensor will detect the metal object interacting with the magnetic field.
The sensor does not react to non-metallic substances such as liquids or dirt. Therefore, the magnetic sensor works effectively in dusty or humid environments.
III. Sensor classification
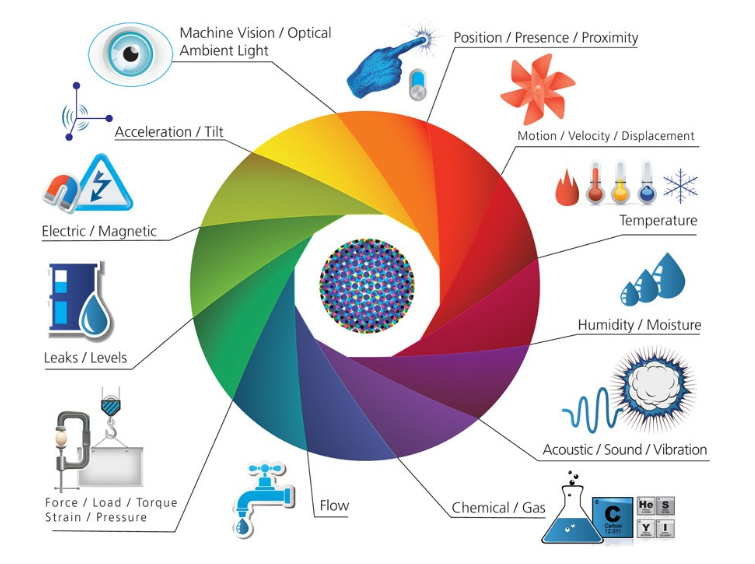
Sensors are divided into the following 6 main types:
1. According to the measurement factor:
Physical sensors: Measure physical factors such as temperature, pressure, light, humidity, and acceleration. For example, temperature sensors measure ambient temperature, pressure sensors measure air or liquid pressure.
Chemical sensors: Used to detect and measure the concentration of chemicals. For example, gas sensors measure CO2 concentration, pH sensors measure the pH of solutions.
Biological sensors: Used in medical and biological applications to measure biological factors such as glucose, DNA, or proteins. For example, glucose sensors measure blood sugar levels.
2. According to the operating principle:
Resistive sensors: Change resistance when the measurement factor changes, such as thermistor sensors.
Capacitive sensors: Change capacitance when the measurement factor changes, such as capacitive pressure sensors.
Electromagnetic sensors: Operate based on electromagnetic phenomena, such as Hall sensors to measure magnetic fields.
3. According to the output signal:
Analog sensors: Generate output signals as a continuous value, such as temperature sensors using thermistors.
Digital sensors: Generate output signals as digital values, such as distance sensors using ultrasonic waves.
4. According to the application:
Industrial sensors: Used in manufacturing processes and industrial automation, such as pressure sensors in pneumatic systems.
Medical sensors: Used in medical devices, such as heart rate sensors and blood oxygen sensors.
Household sensors: Used in household appliances, such as light sensors in smart lights and motion sensors in security systems.
5. By measurement type:
Direct measurement sensor: Measures the element to be measured directly, such as a thermometer measuring body temperature.
Indirect measurement sensor: Measures the element to be measured through intermediate elements, such as an infrared sensor measuring body temperature based on infrared radiation.
6. By level of intelligence:
Traditional sensor: Only performs basic measurement functions without complex signal processing capabilities.
Smart sensor: Integrates signal processing, data analysis, and communication with other devices over the network, such as sensors in IoT systems.
IV. Some common types of sensors today
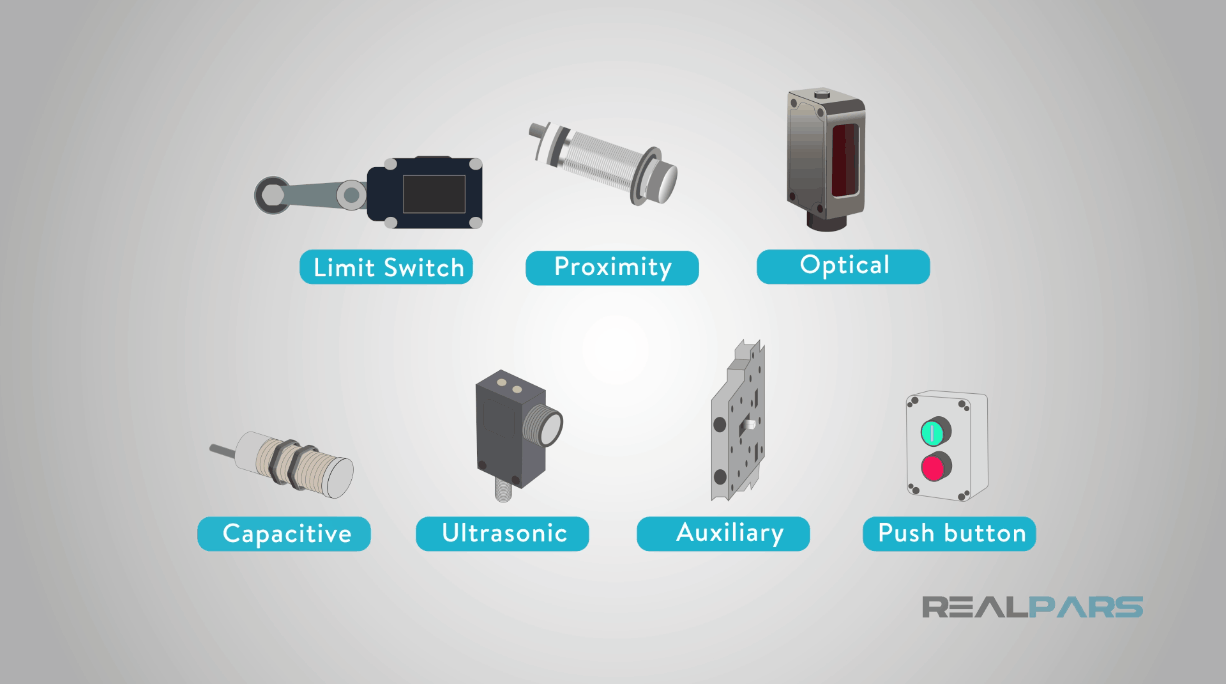
1. Image Sensor
2. Temperature Sensor
3. Accelerometers
4. Radiation Sensors
5. Proximity Sensors
6. Pressure Sensors
7. Position Sensors
8. Photoelectric sensor
9. Smoke sensor
10. Particle sensors
11. Motion sensors
12. Metal sensors
13. Level sensors
14. Leak Sensors
15. Humidity Sensors
16. Gas and chemical sensors
17. Force sensor
18. Flow Sensors
19. Flaw Sensors
20. Flame Sensor
21. Electrical Sensors
22. Contact Sensors
23. Non-contact sensors
V. What are sensors used for?

Sensors are applied in many areas of social life such as in daily life, commercial business, security, air transport, … with many types of sensors such as: thermal sensors, air sensors, sound sensors, color sensors, frequency sensors, magnetic field sensors …
Here are the most common applications you need to refer to:
– In daily life: Sound sensors (eg: clap to turn off the lights), magnetic field sensors (eg: automatically turn off the lights when leaving the room).
– In industrial production: Sensors are mainly used to cut off the current when overloaded, overheated or wet to protect electrical equipment safely …
– In the electronics field: They are used in smartphones, tablets, smart watches and digital cameras.
– In the medical field: Sensors are integrated into devices such as blood pressure monitors, blood glucose meters and ECG machines.
– Industrial: They also use sensors in automation systems, such as pressure sensors and temperature sensors.
– In the transportation sector: optical sensors and distance sensors are used to monitor and control systems.
– In energy production: Used in environmental monitoring such as measuring air quality
– In the fields of robotics and artificial intelligence, sensors help collect data and interact with the world around them.
VI. Notes when choosing to buy sensors
When choosing to buy a sensor, users need to pay attention to the following factors:
– Determine the usage needs: What is the purpose of using the sensor? What quantity needs to be measured? What is the operating environment of the sensor?
– Choose the right type of sensor: There are many different types of sensors with different operating principles and functions. It is necessary to choose the type of sensor that is suitable for the usage needs and operating conditions.
– Technical parameters: Consider the important technical parameters of the sensor such as measuring range, accuracy, sensitivity, response time, etc.
– Price: Compare prices of different suppliers to choose a product that fits your budget.
– Supplier: Choose a reputable supplier to ensure product quality and after-sales service.
Sensors are an indispensable part of modern life, helping us monitor and control the surrounding environment effectively. With the continuous development of technology, sensors are becoming more and more accurate and diverse, bringing many benefits to industries and daily life.
Finally, it is an honor to announce that PMS Co.,Ltd is the “Distributor” of the AGKB-M0524 series inductive proximity sensor product line
With the beginning of this cooperation is a stepping stone for the strong development of the OMCH brand sensor lines – Made in China with quality and reputation will develop on the industrial system of Vietnam in the coming time
Once again, the image of the magnetic proximity sensor line of the OMCH brand appears

















0 Comments